Vietnam vs China Manufacturing: A Detailed Comparison
- Date:
- Author: SVI Content Team
- Share:
Nowadays, the manufacturing world is full of uncertainty as the ongoing shifts in global trade. With the trade tensions between the U.S. and China, more and more companies are reassessing their sourcing strategies looking at alternatives to China for their manufacturing needs, and Vietnam is emerging as a strong contender. But is Vietnam a better location for production?
In this blog, we will explore a detailed comparison of manufacturing in Vietnam vs China, exposing factors like labor costs, manufacturing capabilities, shipping logistics, and trade agreements.
1. Vietnam vs China Comparison: Labor Costs
When China manufacturing moving to Vietnam, cost is at the first tier of the list. Here’s the difference between China vs Vietnam in labor costs.
China: Over the years, labor costs in China have been steadily increasing. The highest minimum wage in 2024 is 2690 CNY (USD$374), while the lowest minimum wage is 1540 CNY (USD$214).
Vietnam: Based on regions, the minimum monthly wages in Vietnam are from 3,450,000 VND (USD$137) to 4,960,000 VND (USD$196).
- Region I: 4,960,000 VND (appro. $196 USD)
- Region II: 4,410,000 VND (appro. $175 USD)
- Region III: 3,860,000 VND (appro. $153 USD)
- Region IV: 3,450,000 VND (appro. $137 USD)
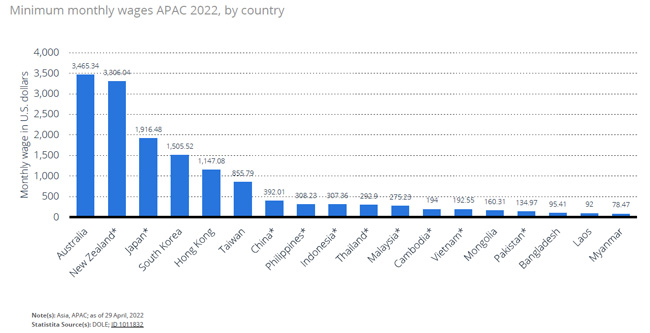
Below is the data about the average minimum monthly wage in China and Vietnam as of 2022. China: $392.01; Vietnam: $192.55.
Besides the labor costs, the overall manufacturing costs also contain indirect manufacturing costs associated with production, such as material, energy costs, space rent, taxes, etc. These cannot provide specific comparisons, but you should take them into account when deciding where to produce your goods.
2. Vietnam vs China Manufacturing Workforce
China’s Labor Force
China is known as the second-largest country in population. The total number of its population is about 1.41 billion.
- Total labor force: According to data, it is about 772.2 million people in 2023.
- Labor force participation rate: 66.4% in December 2023.
- Trend: Showing a general decreasing trend in recent years.
Vietnam’s Labor Force
The country ranks at 16th of the largest population with its total population is 98.86 million in 2023.
- Total labor force: According to Vietnam Law Magazine, it is about 52.4 million people in 2023.
- Labor force participation rate: 68.5% in Q1 2024.
- Trend: Increasing, with growth of 196,600 people over the previous year.
China has a larger and more experienced workforce, which can be advantageous for complex manufacturing processes. Vietnam’s workforce, while growing, may have less experience in certain industries.
3. China vs Vietnam Manufacturing Capabilities
- Cover a wide range of products and capable of producing sophisticated products
- Leader in electronics, machinery and high-tech goods
- Highly developed manufacturing infrastructure
- Robust and diverse supply chain network
- Well-established manufacturing ecosystem
Vietnam: While Vietnam has made significant progress in recent years, the country’s manufacturing sector still faces challenges.
- Rapidly growing manufacturing sector, accounting for over 20% of GDP
- Strong in traditional industries such as textiles, footwear, and furniture
- Growing capabilities in electronics, computers, and components
- Expanding into high-tech manufacturing with investments from major companies
- Developing supply chains, but still dependent on imports for some materials
4. China vs Vietnam Comparison: Material Resource
- Limited natural resources compared to China
- The steel industry is growing rapidly, producing over 16 million tons of steel and 5 million tons of iron a year
- Many industries in Vietnam depend significantly on imported raw materials
China: The country is the 4th largest country in the world by area, and has a pretty substantial resource for manufacturing.
- Rich in rare earth metals, coal, iron ore, and other minerals
- World’s largest producer of many minerals and metals
- Pig iron production reached 72.1 million metric tons in December 2021
- High degree of self-sufficiency in many raw materials
5. China vs Vietnam Shipping Logistics:
Shipping Ports:
Both Vietnam and China have great coastlines. This is convenient for shipping products to the target destinations. China: “China has the world’s largest container port system, with seven of the world’s ten busiest container shipping ports located along China’s coastline—namely the ports of Shanghai, Ningbo-Zhoushan, Guangzhou, Qingdao, Tianjin, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong.” — Research Expert in Statista- According to statistics in 2023, the Port of Shanghai handled over 49 million TEUs (Twenty-foot Equivalent Units), and it is the largest container port in the world.
- China’s ports handled 280 million TEUs of containers, marking a 4.9% year-on-year increase.
- Cargo throughput at ports reached 15.51 billion tonnes in 2023, reflecting an 8.4% year-on-year growth.
Vietnam: The major ports in Vietnam are Ho Chi Minh City, Hai Phong, Cai Mep, and the port of Ho Chi Minh City is the biggest one, handling over 5 million TEUs and ranking 23rd globally in the Lloyd’s 2023 list.
- In 2023, Vietnam’s port system had a total capacity to handle 24.7 million TEUs of containers.
- Vietnam’s cargo throughput was estimated at 756.8 million tons, up by 5% year-on-year based on the report.
Delivery Lead Time:
To ship products to the U.S., the delivery lead time from China and Vietnam is close. Below are the delivery times in both countries to the U.S. market:| Methods (ports to ports) | China to U.S. | Vietnam to U.S. |
|---|---|---|
| Full Container Load (FCL) | 14-35 days | 21-38 days |
| Less than Container Load (LCL) | 14-42 days | 21-45 days |
| Air | 3-10 days | 5-8 days |
| Express | 1-5 days | 1-4 days |
6. China vs Vietnam Policy Incentives:
To compare manufacturing in China vs Vietnam, both countries offer attractive policy incentives to boost foreign investment and economic growth, particularly in high-tech and manufacturing sectors.
China‘s incentive package is extensive, featuring a range of tax benefits, including reduced Corporate Income Tax rates for high-tech enterprises, substantial investment subsidies, and region-specific incentives.
Vietnam is rapidly evolving its policies to compete on the global stage. The country provides preferential tax rates, VAT reductions, and targeted support for high-tech investments and specific sectors like education and renewable energy.
Vietnam’s recent focus on developing its semiconductor industry through planned tax incentives and increased funding to attract cutting-edge technologies.
7. China vs Vietnam Trade Agreements:
China and Vietnam have both established extensive networks of trade agreements to boost their manufacturing sectors and international trade.
China: China has entered into several trade agreements and arrangements with various countries and regions. The most significant recent trade agreement involving China is the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), between 15 countries in the Asia-Pacific region.
Vietnam: Vietnam is a member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), thus taking advantage of ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA). Other trade agreements include Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), RCEP, and also many bilateral Trade agreements (BTAs).
Exporting goods from China to the U.S. has become more difficult due to rising tariffs from the ongoing conflict between them. Meanwhile, Vietnam is also impacted as the new U.S. administration plans to impose tariffs on goods from various countries, including Vietnam. These tariffs threaten the competitiveness and profitability of exports from both nations to the U.S. market.
Conclusion
While China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing, the shifting dynamics of the global market and the need for supply chain diversity have made Southeast Asia, particularly Vietnam, an increasingly attractive alternative. Vietnam’s proximity to China, coupled with its competitive labor costs, growing manufacturing capacity, and favorable business environment, position it as an ideal “China+1” option for companies seeking to mitigate risk.
However, moving manufacturing from China to Vietnam requires careful consideration of various factors.
Whether you’re sourcing from China or Vietnam, you’ll inevitably run into pitfalls you don’t understand. At SVI Global, we offer comprehensive sourcing services to help navigate these obstacles. With offices in both countries, we have in-depth knowledge of the local industries and market trends. Our on-the-ground presence allows us to assist you in sourcing directly from the region, visiting factories, and managing the entire sourcing process. Contact us today!