Indonesia Manufacturing: Key Industrial Sectors & Regions
- Date:
- Author: SVI Content Team
- Share:

Indonesia, a sprawling archipelago with a diverse population and rich natural resources, is fast becoming a focal point in the global manufacturing landscape. It is the largest country in Southeast Asia and the top 10 manufacturing country in the world.
Manufacturing is the biggest industry in Indonesia as it is the largest contributor to the gross domestic product (GDP). According to statistics from Macrotrends, the manufacturing sector accounted for 18.67% of Indonesia’s GDP in 2023. How Indonesia manufacturing contribute significantly to its development?
This blog post will provide an in-depth look into its manufacturing environment, exploring the potential, key manufacturing sectors and manufacturing areas in Indonesia.
Part 1. The Export Landscape: More Than Just Numbers
Indonesia is also the only ASEAN country in the top 10 in terms of global contributions to manufactured goods, accounting for 1.4% of global manufacturing output. This achievement is a significant improvement as Indonesia, which was still in 16th place four years ago, became the largest manufacturing powerhouse in ASEAN this year.
While it’s true that over 70% of Indonesia’s exports remain in Asia, the country is also making inroads into other markets. Approximately 11% of its exports go to North America, and another 10.6% find their way to the European Union.
This geographical diversification is a testament to the quality and competitiveness of Indonesian products. Moreover, Indonesia’s export performance has been on an upward trajectory, reaching its highest level in nearly a decade.
Part 2. Potential of Manufacturing in Indonesia
1) Rich Natural Resources and Raw Materials
As an archipelago, Indonesia is a rich source of resources in Southeast Asia, as it is endowed with rich deposits of coal, oil, and minerals such as copper, gold, nickel and tin. These resources provide a strong impetus for the Indonesia manufacturing industry, and many automobile manufacturers such as Wuling, Toyota, BYD, etc. have gone to Indonesia to invest and build factories.
2) Huge and Youthful Workforce
Population is an important element in the development of a country. According to World Bank, Indonesia’s total population reached about 281 million in 2023, making it the fourth most populous country in the world, after India, China and the United States.
Moreover, the average age of Indonesia’s population is around 30 years old, and only 7.1% of the population is over 65 years old. Against the backdrop of ageing populations in many countries, Indonesia’s youthful demographic structure gives the manufacturing industry an advantage in terms of labor force.
3) Large and Growing Domestic Market
Indonesia’s GDP has maintained a growth rate of 5% in the past few years, driven by policies and population rejuvenation, Indonesia’s emerging market economy continues to develop and per capita income increases, the middle class is gradually expanding, it is expected that by 2030 the middle class will increase by 75 million people, so it is bound to increase the level of consumption in Indonesia as well.
4) Low Labor Costs
Indonesia is a lower labor cost country in Southeast Asia, for example, in Central Java, which is dominated by labor-intensive industries, according to data from WageIndicator, the minimum labor wage in Central Java is about 125 USD/month; while in the capital city of Jakarta, the minimum monthly salary is raised to IDR 5,067,381, or about 308 USD/month.
5) Favorable Government Stategics and Incentives
The Indonesian government launched the “Industry 4.0” program in 2018 to boost the country’s economy by vigorously developing manufacturing technologies. Food & beverages, textile and apparel, automotive, electronics and other key industries have been designated as priority industries for support by the government, which plans to increase the economic growth rate of these industries by two percentage points per year by 2030, creating more than 10 million jobs.
For Indonesia manufacturing industry, the government is currently improving the investment environment to create better conditions for attracting investment, such as improving government services, streamlining the investment approval process, increasing infrastructure construction, and improving the supply chain.
6) Strategic Location for Global Supply Chains
Located in Southeast Asia, a strategic location at the crossroads of Asia and the Pacific, Indonesia consists of multiple islands and is the largest archipelagic country in the world. The country is bordered by Malaysia and is close to other large Asian markets such as China, India and Japan.
7) Strategic Partnerships
Indonesia is a member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), which has signed free trade agreements with a number of countries, including Australia, New Zealand, China, South Korea and Japan. As an individual market, Indonesia has also entered into bilateral free trade agreements with other countries such as Chile, Mozambique, Iceland, Norway, Switzerland and Liechtenstein, and is in the process of negotiating with India, Turkey, the European Union and Tunisia.
These trade agreements provide Indonesian consumers and businesses with improved market access for goods and services, new technologies, and investment opportunities.
Part 3. Key Manufacturing Industries in Indonesia
Wonder what products are made in Indonesia? Below are the top 5 industries in Indonesia. This list is in no particular order.
1) Automotive Industry:
Indonesia is the largest consumer of automobiles in ASEAN, with motor vehicle sales reaching 1,048,000 units as of 2022, much higher than other countries.
The automotive market still has room because the car ownership is at a low level. Besides, plus the resource advantage we mentioned above, the government’s nickel export ban and policy support drive many automotive manufacturers build factories in Indonesia, including Daihatsu, Toyota, Mazda, BMW, Chery, and Mitsubishi.
2) Electronics Industry:
The electronics industry in Indonesia has witnessed notable growth, fueled by the needs of the domestic market. The country has been successful in attracting investments in electronics manufacturing, including the production of components, consumer electronics, and telecommunications equipment.
The rapid increase of Internet users in Indonesia has made smartphones, laptops, telecommunication devices, and remote devices the biggest beneficiaries. According to a report by International Data Corporation (IDC), smartphone shipments in Indonesia have long exceeded 49.31 million units in 2023, an increase of about 8.9%.
3) Textile & Apparel Industry:
Indonesia has a rich history in the textile and apparel industry. It is the leading textile and apparel producer which have a well-established supply chain covering the entire production process and multiple textile manufacturing clusters across the country.
The textile & apparel industry in Indonesia is an important pillar of the national economy, not only does it provide employment for nearly 2 million people, but significantly, promotes skills development, innovation and entrepreneurship that benefit its GDP. In 2022, exports of textiles and apparel from Indonesia were valued at $12 billion.
4) Food & Beverages Industry:
Indonesia’s food and beverage industry accounts for as much as 33.9% of the manufacturing industry, far more than other subsectors. With its wealth of natural resources like coffee, cocoa and palm oil, Indonesia provides a stable supply of raw materials for this industry.
It is one of the priority industries in Indonesia’s “Industry 4.0,” and the government aims to build an ASEAN food and beverage powerhouse, which may possess greater potential for development.
5) Chemical Industry:
The chemical manufacturing sector in Indonesia is the key contributor to the GDP and exports.
GDP: In 2022, the chemical industry was responsible for 10.5% of Indonesia’s GDP, and it is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 5.5% over the next five years.
Exports: In 2022, the industry exported $40 billion worth of products, accounting for 12% of Indonesia’s total exports.
During the period from 2020 to 2030, the government has planned to invest heavily in the petrochemical industry, investing a total of $31 billion in large-scale chemical plant construction projects. This will strengthen the upstream chemical sector to produce import-substituting petrochemical products.
Part 4. Major Manufacturing Areas in Indonesia
Indonesia is home to several major manufacturing areas. Let’s explore some of the Indonesia manufacturing centers.
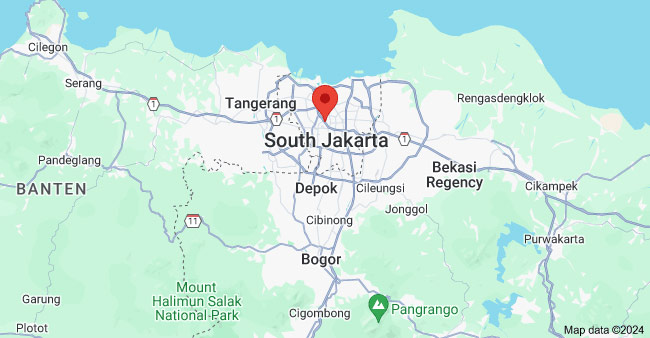
1) Jakarta and Greater Jakarta (Jabodetabek)
Jakarta is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. It bears manifold urban functions as the center of politics, commerce, finance, services, trade, culture and education in Indonesia.
Jakarta and its surrounding regions, collectively known as Jabodetabek, form a prominent manufacturing hub. These areas host a concentration of industrial estates and manufacturing facilities, attracting both domestic and foreign investments.
Major Cities: Jakarta, Tangerang, Bekasi, Bogor, Depok
Key Industries: Automotive, Electronics, and Food & Beverage
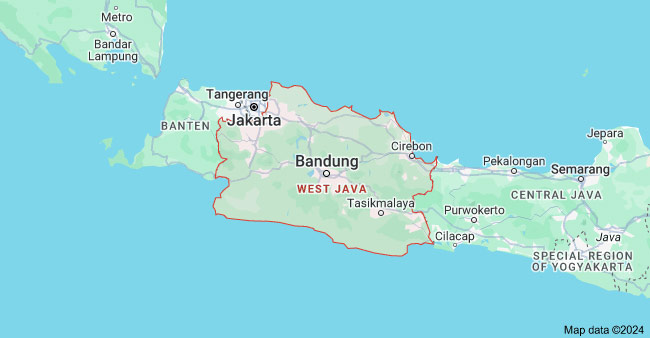
2) West Java
West Java is another significant manufacturing hub in Indonesia. It is one of the most dynamic economic regions in Indonesia, located in the western part of the island of Java and neighboring Jakarta to the northwest.
Given its proximity to the capital city of Jakarta and its economic impact, West Java has developed into a support area for Jakarta, boosting the province’s economy. 60% of Indonesia’s manufacturing operations are based here, including industries like textiles, automotive, machinery and electronics.
Major Cities: Bandung, Bekasi, Cikarang, and Purwakarta, Karawang
Key Industries: Textiles, Automotive, Electronics, Food & Beverage
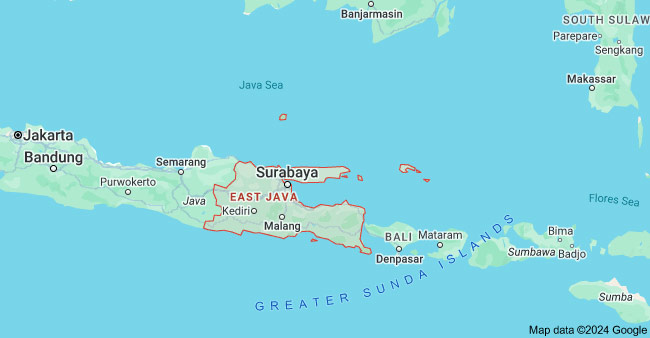
3) East Java
East Java is located in the northeastern corner of the island of Java and it contributes more than 15% to Indonesia’s GDP. Its capital, Surabaya, is the largest city in East Java and the second largest city in Indonesia after Jakarta. Surabaya is of great economic value and has been one of the busiest and most important trading city ports in Asia since the early 20th century.
The province is host to various types of industries, with many large industries situated here, such as the largest shipyard (PT PAL) and cement factories (Semen Indonesia & Semen Holcim), as well as the country’s largest e-cigarette OEM, Smol by the end of 2021.
Major Cities: Surabaya
Key Industries: Electronics & Appliance, Food & Beverage, Machinery Equipment, Shipbuilding, Toys
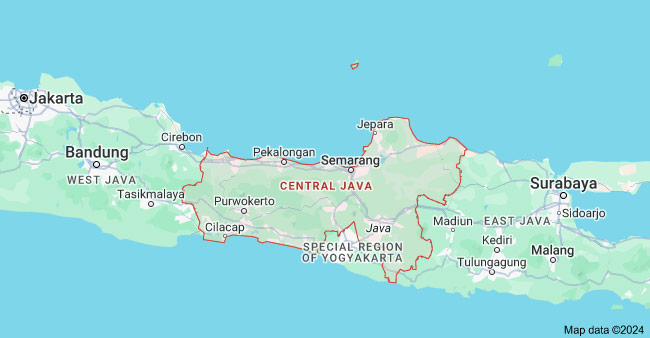
4) Central Java
Central Java is a significant manufacturing region in Indonesia. In the 2022 GDP of the province, the share of the manufacturing industry is about 34%, which is highly reliant on the development of it. And the main sector is to produce textile and apparel manufactured products in Indonesia, which accounts for 56% of the investment. The province has developed infrastructure with 11 seaports and 5 commercial airports.
Semarang, as the capital of Central Java, is an important industrial city and the fifth largest city in Indonesia. It has a strategic location for the imports and enjoys a major port, Tanjung Maas.
Major Cities: Semarang
Key Industries: Textile & Apparel, Nonmetallic Minerals, Food & Beverage
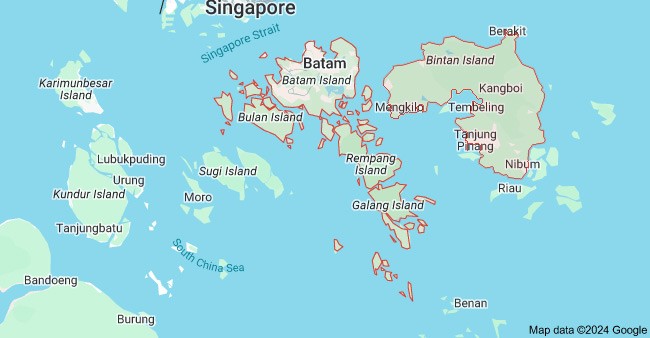
5) Batam and Bintan Islands
Batam and Bintan, situated in the Riau Islands province, are close to Singapore, with Batam being at least 5.8 kilometers away from the Singapore Strait. This unique location has positioned the two islands as industrial cities that are attracting investment from the electronics and shipbuilding industries.
Batam and Bintan offer free trade zones and incentives for Indonesia manufacturing companies. They are two out of four existing free trade areas in Indonesia. This makes them attractive destinations for foreign investment.
Additionally, Batam is one of the four tariff-free zones in Indonesia, which is close to the city’s port and serves as a distribution point for international cargo ports.
Major Cities: Batam, Bintan
Key Industries: Electronics, Machinery, Shipbuilding, Petroleum, Semiconductors, ICT
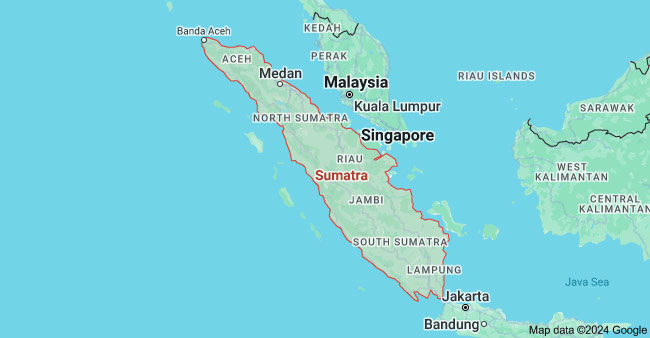
6) Sumatra
Sumatra, one of Indonesia’s largest islands, is home to key manufacturing hubs and industries. The island is located in the West of Indonesia, with sound infrastructure and a huge population. It is strategically located near the Straits of Malacca to the east, which connects the Indian and Pacific Oceans, and is an internationally important transportation and trade hub center.
The region is known for palm oil processing, rubber production, and other agricultural-based industries. In addition, manufacturing products such as automobiles and machinery also contribute to its growth.
Major Cities: Medan and Palembang
Key Industries: Plam Oil, Rubber, Food & Beverage, Chemicals, Metal
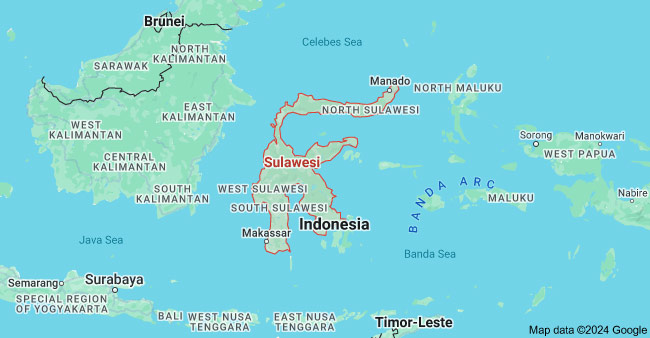
7) Sulawesi
Sulawesi is the most resource-rich island in Indonesia, and is a major source of palm oil, coal, petroleum, bauxite, and timber. It is a region with diverse industries, including nickel mining and processing, agriculture, and fisheries. However, the region’s infrastructure is poor, and the government has begun to move the capital from Jakarta, which will provide a lot of business opportunities. and fisheries.
Moreover, the Indonesia Morowali Industrial Park in Sulawesi has made great development in the past few years. It helped Sulawesi turn into the nickel capital of the world.
Major Cities: Makassar, Gorontalo
Key Industries: Mining and Mineral, Metal and Steel, Plam Oil, Textile, Paper, Food & Beverage
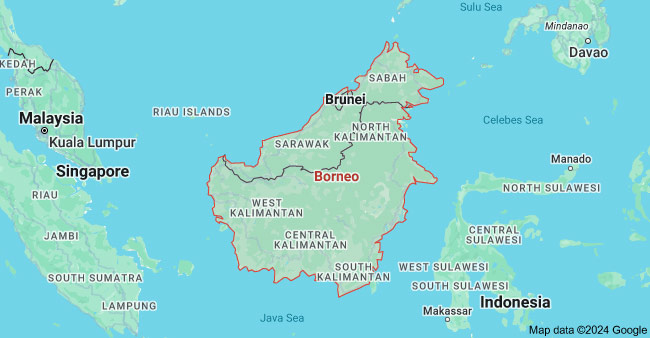
8) Kalimantan
Kalimantan, known for its rich natural resources, has key manufacturing sectors such as timber processing and mining. The region’s timber industry plays a vital role in processing and exporting wood products, while mining activities focus on coal and other minerals.
Nusantara in East Kalimantan will replace Jakarta as the future capital of Indonesia. In 2022, the Indonesian parliament passed a bill authorizing the relocation of the capital from Jakarta to East Kalimantan province. The formal opening of the new capital is scheduled for August 17, 2024, coinciding with Indonesia’s Independence Day. This will bring notable development potential to the city.
Major Cities: Pontianak, Balikpapan, Samarinda, Nusantara
Key Industries: Palm Oil, Petroleum, Mining and Mineral, Wood, Rubber
Part 5. Challenges of Manufacturing in Indonesia
1. Limited Domestic Supply Chain
Indonesia, for now, is heavily reliant on imports for manufacturing components. This gap forces companies to struggle with meeting local content rules which require products to be made domestically.2. High Production Cost
Dependence on imported materials and incomplete supply chains elevate production expenses. These higher costs erode the competitive edge of Indonesian manufacturers and make the country tougher to attract and sustain foreign investment in the global market.3. Heavy-Handed Protectionism
The Indonesian government is committed to transforming the country from a consumer market into a high-tech manufacturing hub. Strict local content mandates are meant to boost domestic manufacturing but may inadvertently deter foreign investors if compliance proves impractical.4. Regulatory Complexity
Cumbersome permit processes, redundant procedures, and inconsistent legal frameworks create significant hurdles for investors. A lack of transparent rules and dependable infrastructure makes it challenging for businesses to operate efficiently, stifling investment and growth in manufacturing.5. Weak Intellectual Property Protections
Based on the report of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, Indonesia’s low ranking on international IP indices raises concerns about patent and trademark security. This weak protection environment could discourage high-tech investors from committing long term.6. Infrastructure Gaps
Inefficient port operations and high transportation costs lead to unreliable logistics and increased operational expenses. These infrastructure challenges further diminish the competitiveness of Indonesia’s manufacturing sector.Part 6. Will You Find a Good Manufacturer in Indonesia?
Indonesia manufacturing sector, in terms of the country’s Standard Business Classification (Klasifikasi Baku Lapangan Usaha or KBLI), comprises 24 sub-sectors, ranging from Food and Beverages to machine maintenance and installation.
Indonesia’s diverse manufacturing capabilities make it an ideal sourcing destination for a wide range of manufacturing products in Indonesia. Its strategic location, resources and growing influence in regional and global markets make it a compelling choice for businesses looking to diversify their sourcing strategies in Southeast Asia.
In the intricate world of outsourcing, especially in a diverse landscape like Indonesia manufacturing, expertise is paramount. Professional teams are best equipped to handle specialized tasks, ensuring efficiency and precision.
SVI Global, with 2 decades of dedicated experience in the realm of outsourcing, is intimately familiar with Indonesia major industries, environment and policies. Our deep-rooted knowledge and connections make the process of finding the right factory in Indonesia not just easier, but also more strategic and effective. If you’re considering outsourcing in Indonesia, trust the experts. Reach out to SVI Global and let us guide you through a seamless and successful outsourcing journey.