Lean Manufacturing: Driving Efficiency and Cost Reduction
- Date:
- Author: SVI Content Team
- Share:
As industries worldwide strive to optimize their operations, enhance efficiencies, and deliver value to their customers, one methodology and strategy have emerged as the frontrunner: Lean manufacturing. This revolutionary approach is transforming the manufacturing industry and inspiring companies across diverse sectors.
With its roots in the principles developed by Toyota in the mid-20th century, lean manufacturing has become a beacon of excellence, changing businesses and redefining industry management standards.
So, what exactly is lean manufacturing? In this article, we will explore the definition and root principles of lean manufacturing, showing how these principles can empower organizations to increase efficiency, reduce costs, improve quality, shorten lead times, and achieve sustainable growth. Let’s get started.
Part 1. What Is Lean Manufacturing?
Do you know the lean manufacturing definition?
Lean manufacturing is a methodology or approach to manufacturing and operations management.
The main objective of lean manufacturing is to eliminate waste, optimize processes, reduce customer response times and create value for customers.
Lean manufacturing has its roots in the Toyota Production System (TPS), which was developed by Toyota Motor Corporation in Japan in the 1950s and 1960s. The system was primarily developed by Taiichi Ohno, Shigeo Shingo, and other Toyota engineers and managers.
It can be traced back to the aftermath of World War II when Toyota faced resource constraints and intense competition. Toyota aimed to find ways to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and increase productivity despite limited resources.
Lean manufacturing has become a well-recognized method of process improvement and is used in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, services, and software development. By adopting lean principles, organizations can achieve operational excellence and gain a competitive edge.
Part 2. Principles of Lean Manufacturing
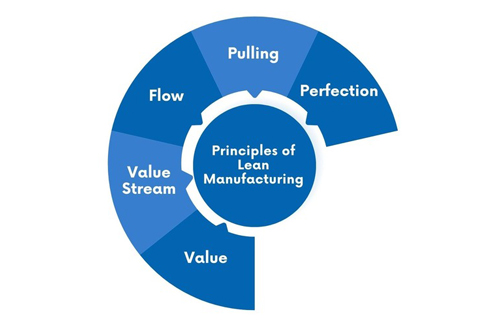
Lean manufacturing principles developed by Taiichi Ohno are the basis of understanding the lean methodology. And 5 core principles of lean manufacturing include Value, the Value Stream, Flow, Pull and Perfection.
1. Identify Value
At the core of lean manufacturing is understanding the value desired by the customer – what customers want from buying a product. Companies should create value for customers first, and only then can they deliver value to themselves while meeting customer value.
By aligning processes with customer needs, manufacturers can optimize resource utilization and eliminate activities that do not add value, such as overproduction and excess inventory.
2. Map the Value Stream
The value stream mapping is to analyze and visualize the flow of materials cost, information and activities within a product life cycle. It provides a 360° view of the entire process and helps distinguish between value-adding and non-value-adding activities, thus creating a map of the future state and reducing waiting times.
3. Create Flow
Once the group has developed the value stream map, it can create a flow based on it. A continuous workflow will eliminate unnecessary steps, reduce excessive movement and keep the steps that add value for customers with efficiency. With it, companies can achieve seamless operations, reduce lead time and improve overall productivity.
4. Establish a Pull System
Lean manufacturing emphasizes a pull-based approach, where production is driven by actual customer demand, rather than by forecasts or predetermined schedules.
The pull system used the Just-In-Time (JIT) method to ensure manufacturers deliver products on time and with high quality while using a profitable way. It can minimize overproduction and reduce inventory. What’s more, this principle allows companies to respond efficiently to quickly adapt to customer demands and improve customer satisfaction.
5. Pursue Perfection
“Perfection” is a core principle of lean manufacturing. Pursuing perfection involves identifying areas that need to be improved and seeking ways to reduce waste and minimize the whole production time. By continuously striving for perfection, companies can foster a culture of continuous improvement and cultivate innovation.
Part 3. Benefits of Lean Manufacturing
Why lean manufacturing is so popular in industries? You cannot go away from the advantages of that.
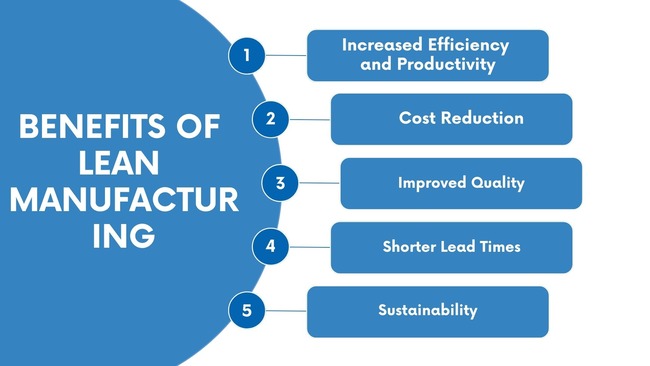
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
One of the benefits of lean manufacturing is its ability to enhance efficiency and productivity. Lean manufacturing focuses on identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities and developing an uninterrupted flow of work. This contributes to improving operational efficiency and productivity.
2. Cost Reduction
Lean manufacturing is a customer-centric approach, producing what is needed when it is needed. The value identification and cost analysis help reduce waste in inventory, defects, overproduction and overprocessing. By doing this, companies can reduce the overall cost associated with carrying inventory, rework and excess resources.
3. Improved Quality
Lean principles focus on standardizing work procedures, error-proofing processes, and empowering employees to identify and address quality issues promptly. The emphasis on continuous improvement also encourages dealing with quality concerns proactively. This results in improved product quality, customer satisfaction, and reduced rework.
Lean manufacturing streamlines processes, minimizes waiting time and reduces cycle times, which enables manufacturers to deliver products faster, respond quickly to customer demand, and gain a competitive advantage.
5. Sustainability
Lean manufacturing promotes responsible resource utilization and waste reduction with environmentally friendly technologies. Companies that strive for less waste and innovation can better adapt to the market, achieve green production and contribute to sustainable development.
Part 4. FAQs about Lean Manufacturing
1. What Are the Popular Tools and Techniques for Lean Manufacturing?
The 5 lean manufacturing tools and techniques are:
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM): It is a technique used to visualize and analyze the flow of materials, information, and activities required to deliver a product or service.
- 5S: It is for workplace organization, consisting of five steps: Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain.
- Kanban: It is a visual system used to control and manage workflow.
- Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): It is a methodology for businesses to continuously improve activities by involving all employees.
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM): It is an approach to equipment maintenance aimed at maximizing machine availability, efficiency, and reliability.
2. Are There Risks to Applying Lean Manufacturing?
Despite the excellent benefits of lean manufacturing for production, it is important not to overlook any potential risks while adopting this methodology to make a positive impact. The following are the risks you should consider.
- Overemphasis on Zero Defects
- Overemphasis on Cost Reduction
- Lack of Adequate Planning and Execution
- Neglect of Employee Needs and Motivation
- Staff Shortage or Turnover
- Neglect of Maintenance of Production Equipment
- Potential Supply Chain Disruptions
3. What Are Two Characteristics of Lean Manufacturing?
The key characteristics of lean manufacturing: Just-in-time (JIT) production and continuous improvement (Kaizen).
4. What Are the Types of Wastes in Lean Manufacturing?
Wastes, in lean manufacturing, refer to any activities or processes that do not add value to the final product or service. These wastes are obstacles that hinder efficiency, productivity, and overall process improvement.
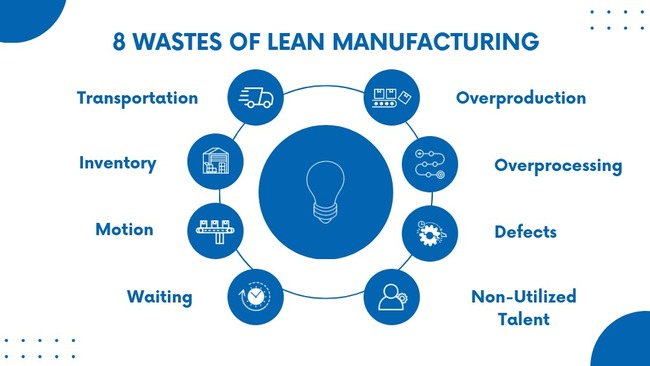
There are several types of waste identified in lean manufacturing. The original 7 wastes are first formulated by Toyota engineer Shigeo Shingo in the 1950s. Later the Non-Utilized Talent was included in the 1990s after TPS was adopted in the Western World, and now there are 8 wastes of lean manufacturing.
- Transportation—Unnecessary movement or transportation of materials, products, or information due to the factory layout.
- Inventory—Excess stock or inventory of raw materials, work-in-progress, or finished goods.
- Motion—Unnecessary or excessive movement of people or equipment within a process.
- Waiting—Idle time or delays resulting from waiting for materials, information, manpower, equipment, or approvals.
- Overproduction—Producing more than what is actually needed, or producing before a customer’s request.
- Overprocessing—Carrying out more work or using more resources than necessary.
- Defects—Products or services provided not meeting quality standards or customer requirements
- Non-Utilized Talent—Failing to fully utilize the potential of employees.
Part 5. Conclusion
The management philosophy of lean manufacturing is far-reaching, and many of the world’s Fortune 500 companies have learned from Toyota’s approach to production management. Lean manufacturing provides a powerful framework for organizations to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and deliver superior value to customers.
The goal of lean manufacturing is to reduce waste and create value for customers, which facilitates businesses to gain efficiencies, lower costs, improve quality and achieve sustainable growth by aligning with its principles. It is a proven methodology for organizations to respond to rapidly changing market trends and drive success in the current society.
But the most important in a successful lean system is RESPECT. This entails not only respecting customers but also, crucially, respecting employees. Lean manufacturing encourages employee involvement to drive process improvements and create a better work environment.
If your company is seeking efficient outsourcing solutions, look no further than SVI Global. We specialize in managing the supply chain and identifying the most suitable suppliers who prioritize productivity and high quality. We put our customers as our priority and treat our suppliers with the same respect as we want. Our goal is to provide value that matches your needs. For more information, welcome to Contact Us at any time and we will provide a service tailored to your requirements