Supplier Relationship Management: Why It's More Than Just a Business Strategy
- Date:
- Author: SVI Content Team
- Share:

In business cooperation, the significance of effective communication and collaboration cannot be overstated, particularly when it comes to successful supply chain management. Suppliers hold a critical position in maintaining a seamless flow of supply chain processes. Without suppliers, production would come to a standstill, just like a symphony orchestra without its musicians. Thus, the importance of supplier relationship management (SRM) becomes evident, as it enables companies to cultivate favorable and mutually beneficial relationships with their suppliers.
Next, this text will focus on the topic of supplier relationship management, providing an understanding of the SRM definition and its importance, and illustrating how SRM can be implemented to help companies create a strong supplier network and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Part 1. What Is Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
1. Supplier Relationship Management Meaning
“Supplier relationship management (SRM) is the systematic, enterprise-wide assessment of suppliers’ strengths, performance and capabilities with respect to overall business strategy, determination of what activities to engage in with different suppliers, and planning and execution of all interactions with suppliers, in a coordinated fashion across the relationship life cycle, to maximize the value realized through those interactions.” — From Wikipedia
Based upon the supplier relationship management definition from Wikipedia, SRM is a set of practices and strategies that companies use to effectively build and manage their relationships with suppliers. It is an important element of supply chain management.
The goal of SRM is to maximize the value derived from interactions and create a win-win situation for both the organization and its suppliers. It focuses on establishing transparent and open communication channels with suppliers, understanding their capabilities, and aligning their objectives with companies’ strategic goals. By fostering collaborative relationships, companies can optimize outcomes and achieve their strategic objectives.
2. Why Supplier Relationship Management Is Important for a Business
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) is a crucial business strategy for organizations of all sizes, offering a range of advantages. From the initial supplier selection to ongoing strategic improvements, SRM involves assessing supplier capabilities, monitoring performance, implementing appropriate performance metrics, and establishing effective and transparent communication channels to promptly address any issues that may arise. The following benefits are derived from effective SRM implementation:
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) is a crucial business strategy for organizations of all sizes, offering a range of advantages. From the initial supplier selection to ongoing strategic improvements, SRM involves assessing supplier capabilities, monitoring performance, implementing appropriate performance metrics, and establishing effective and transparent communication channels to promptly address any issues that may arise. The following benefits are derived from effective SRM implementation:
Benefits of Supplier Relationship Management
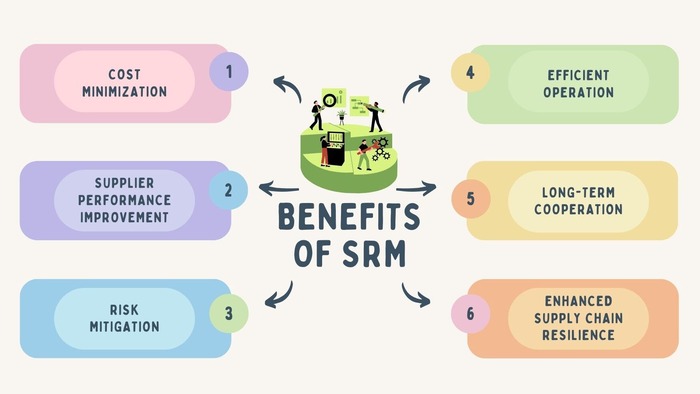
- Cost Minimization: Through building close cooperation and conducting effective negotiations with suppliers, companies can achieve cost reduction, minimizing manufacturing costs, logistics costs and so on.
- Supplier Performance Improvement: SRM facilitates the development of robust product quality standards and performance assessment. With the help of monitoring suppliers’ performance and providing regular feedback, companies are able to promote product quality improvement, ensuring that products or services meet or exceed expectations.
- Risk Mitigation: Implementing SRM allows organizations to better understand and manage supplier-related risks. By conducting thorough risk assessments in IP protection, compliance regulations and more, implementing risk mitigation strategies, and maintaining open communication channels, they can proactively address potential disruptions and minimize losses.
- Efficient Operation: SRM establishes a framework for regular supplier monitoring, feedback, and issue resolution. This lets enterprises optimize related processes, reduce the time and effort required to manage suppliers, and maintain stable and efficient supplier relationships.
- Long-term Cooperation and Strategic Partnership: SRM is committed to establishing long-term cooperation and strategic partnership. Enterprises can build trust and commitment over time by cultivating a deep understanding of each party’s interests and aligning goals. This paves the way for strategic planning, shared risk and reward, etc.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Resilience: Companies can enhance their supply chain resilience through effective SRM. By diversifying and strengthening their supplier base, they can mitigate the impact of disruptions, adapt to changing market conditions, and maintain uninterrupted operations.
Part 2. How to Manage Supplier Relationships
1. Segmenting Supplier Groups
Suppliers are segmented into different groups based on factors such as the services they provide, the company’s goals, and strategies. These groups can include strategic, tactical, or tail suppliers. Each group requires different management approaches. Supplier segmentation provides valuable information for future supplier selection, making the process more effective in identifying suitable suppliers and facilitating supplier evaluation.

2. Customizing Strategies and Objectives for SRM Programs
SRM programs should be tailored to align with the company’s overall business objectives. These objectives may focus on cost reduction, innovation, time savings, or other specific goals. Depending on the type of company, there are varying strategies and objectives. Based on these goals, it is helpful to select the right suppliers and establish specific criteria for supplier evaluation.

3. Measuring Supplier Performance
In line with the customized SRM program objectives, companies can set specific performance metrics for each supplier group to assess their performance against agreed-upon targets. Metrics can include factors like on-time delivery, quality, responsiveness, innovation, or sustainability. Continuously monitoring and evaluating supplier performance using these metrics helps companies provide feedback and address any performance gaps to drive continuous improvement.

4. Developing Supplier Management Plans
Create detailed plans for managing relationships and interactions with each supplier group. Outline communication channels, frequency of meetings, reporting requirements, and collaboration initiatives. Besides, clarify the roles and responsibilities of each member within the team, ensuring that both the company and the suppliers understand their obligations and expectations. Engaging suppliers and providing them with the necessary information in these plans develop collaboration and help achieve strategic objectives.

5. Communicating and Collaborating in a Transparent Manner
Open and honest communication serves as the foundation for building trust in successful business collaborations. Transparent discussions and information sharing on suppliers’ performance foster mutual understanding and facilitate effective collaboration between companies and suppliers. It enables both parties to openly discuss expectations, challenges, and opportunities and then leads to stronger relationships and shared success.

6. Continuous Improvement of Supplier Relationship Management Strategies
Supplier relationship management strategies should be continuously reviewed and improved to adapt to evolving business needs and market dynamics. Regular evaluation of the effectiveness of SRM programs allows companies to discover enhancements and implement necessary adjustments.
SRM aims to establish and maintain long-lasting and fruitful relationships with suppliers. This indicates that SRM goes beyond immediate gains and focuses on fostering sustained collaboration and mutual growth. The relationships and continuous improvement make companies able to unlock the full potential of their supplier network and create a foundation for strategic advantages in the long run.

Part 3. FAQs about Supplier Relationship Management
Q1. What Is the Difference between SCM and SRM
(SCM) Supply Chain Management: Supply chain management refers to a comprehensive management methodology that manages the entire process from production, and transportation to sales of a product, with activities including planning, sourcing, production, distribution and after-sales activities in the supply chain. The goal of SCM is to optimize the efficiency of each link in the supply chain and to reduce the cost and risk of operations.
(SRM) Supplier Relationship Management: Supplier relationship management, as we mentioned in Part 1, is a business strategy to build relationships with suppliers by conducting a comprehensive assessment of supplier capabilities and performance, etc. SRM activities are focused on developing plans, and goals, and managing relationships to build strong partnerships. Through SRM, companies can reduce sourcing costs and increase profitability and competitiveness.
SCM and SRM are two very important concepts in the field of supply chain operations. SCM is a more broadly defined concept that encompasses multiple aspects of the supply chain, while SRM is a specific and relatively independent subset of it that focuses on the maintenance and management of supplier relationships.
Q2. What Are the Challenges of SRM?
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) brings benefits to organizations, but it’s important to acknowledge that effectively managing supplier relationships can be a challenging process. Here are some of the common challenges in SRM:
- Time and effort required to find suppliers that meet the company’s requirements and strategic goals.
- Difficulties in establishing and maintaining open and transparent communication channels with multiple suppliers.
- Challenges in ensuring consistent product quality across various suppliers.
- Communication barriers arising from working with diverse suppliers.
- Potential risks associated with suppliers, environment, society, etc.
- Challenges in managing data and ensuring its security.
Part 4. Wrapping Up
Overall, supplier relationship management is a critical strategy for companies seeking to optimize their supplier partnerships and realize their objectives. SRM offers numerous advantages for companies, including cutting costs, enhancing supplier performance, increasing efficiency and more. However, SRM also comes with its share of challenges. Managing supplier relationships can be a complex task that requires careful attention and proactive strategies.
To establish a robust SRM framework, organizations should set clear goals, implement effective communication strategies, define performance metrics, and continuously update their practices. With these actions, companies can foster resilient and long-lasting relationships with their suppliers.
SRM is not a short-term tactic; it is an enduring and integral business strategy. Companies with experience in the supply chain field tend to be more comfortable with SRM practices. When dealing with the supply chain, finding the right partner can save a significant amount of time. SVI Global, with its extensive experience in supply chain management, offers services to assist companies worldwide. Our company has its service team in countries across the world, including the U.S., China, Mexico, India and other promising countries. We have a vast network of reliable suppliers, enabling us to quickly identify factories that meet specific requirements while assuring clients of product quality and timely delivery.
If you are interested in outsourcing services in supply chain management, we are here to provide assistance and support at any time.